Having a forex trading strategy that’s based on analyzing the news and what’s happening all around the world can be daunting, what with today’s fast-paced news industry and continuous breaking updates. Fortunately, there are some currency pairs that are more suited to traders who prefer looking at specific events and data. One such pair is AUDNZD.
To trade the AUDNZD pair:
- Choose a broker and create a trading account.
- Choose a trading and charting platform.
- Create a trading strategy.
- Analyze the market to determine if AUD will strengthen or weaken against NZD.
- Open a trade (go long or short) based on your analysis and set risk management orders.
- Monitor and close your trade.
Also known as the Aussie/Kiwi, AUDNZD is made up of what are considered risk-on currencies. Trading two risk-on currencies makes your trading strategy more robust since you avoid situations where your strategy is wrecked by factors such as big socio-economic and political news. Let’s look more closely at the AUDNZD combination.
Table of Contents
Currency Chart and Pair Profile
The AUDNZD currency pair comprises two Australasian currencies, the Australian dollar (AUD) and the New Zealand dollar (NZD). Since the pair doesn’t include the U.S. dollar, it’s known as a cross. The AUDNZD cross provides a view of the relative demand for the two currencies by expressing the AUD in terms of the NZD.
The economies behind AUDNZD
Australia is among the world’s top twenty largest economies, ranking 14th in terms of GDP. New Zealand ranks at number 52. Both countries have a significant dependence on commodity exports. Australia is a major exporter of metals and energy products while New Zealand is one of the world’s top milk, meat, and wool exporters. Tourism also forms a significant part of New Zealand’s economy.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) are the two central banks responsible for issuing and managing the Australian dollar and New Zealand dollar, respectively.
What influences the movement of AUDNZD?
Besides the similar geographical location and substantial reliance on trading natural resources, New Zealand and Australia are also big trade partners. This is why the AUDNZD cross tends to be affected by factors in the local economy rather than global factors or risk trends such as the volatility that comes with the US market.
Interest rates, monetary policies, and economic outlook
AUDNZD is greatly affected by domestic monetary policies, interest rates, and other economic data. For instance, interventions and comments from the RBA can move the pair quite a lot. This is why it’s a good idea to pay special attention to the economic outlook and interest rates of both Australia and New Zealand.
Weather patterns, commodity output, and tourism
Since both Australia and New Zealand’s economies are commodity-based and New Zealand has a big tourism sector, AUDNZD is usually sensitive to weather patterns, commodity output, and New Zealand’s tourism sector outlook.
For example, bad weather in either Australia or New Zealand tends often leads to a sell-off of the affected country’s currency. Again, it’s a good idea to keep up with reports on things such as mining output, metal prices, crop planting, harvests, and tourism growth.
Exposure to Asia
Over the years, both New Zealand and Australia have seen some major growth in demand for raw materials from Asian countries including China, India, and Japan. This means that the value of AUDNZD is closely tied to the demand for resources from Asia.
Is the AUDNZD an exotic pair?
The AUDNZD is not an exotic pair. It’s a minor pair. A minor pair is one that doesn’t consist of the U.S. dollar, but has any two of the remaining seven major currencies (AUD, NZD, CAD, EUR, GBP, CHF, and JPY).
Pros of trading AUDNZD
The AUDNZD cross has several characteristics that will give you an edge in the competitive forex market.
- AUDNZD is usually not seriously affected by global headlines. There are hardly ever any top stories and external events that will throw off any good technical analysis. This means that you can create a robust, technical analysis strategy.
- The pair tends to trend often and strongly. This makes it relatively easier to trade compared to other pairs such as EUR/USD which can take a long time to form any obvious trends.
- Although it’s not one of the most volatile pairs in the forex market, AUDNZD still provides enough volatility to make trading worthwhile.
- AUDNZD has an early timezone advantage. Most news for the pair comes early in the trading day, therefore, you can adjust your positions in case of any unexpected events or unfavorable market movement. The early time zone also typically leaves quite a lot of room for the market to correct itself and take a favorable direction.
Cons of trading AUDNZD
Despite providing several benefits, you still have to be alert when trading AUDNZD because it does have some drawbacks.
- Although AUDNZD is largely risk-neutral, it’s still viewed as a slightly riskier pair to trade since, in general, it has less liquidity than the major forex pairs. Consequently, the pair will typically come with wider spreads. This can be especially challenging for day traders who rely on low spreads.
- The lower liquidity of AUDNZD can occasionally result in delays in obtaining market prices and it frequently leads to more slippage. This can cause significant losses when trading.
- AUDNZD trading times may not be the most exciting. Most AUDNZD trading happens during the Asian trading session. However, this session is normally the quietest and slowest in the forex market, so you may not always see a lot of market action. This leads to an important question, “What is the best time to trade AUDNZD?”
The Best Time to Trade AUDNZD
Most AUDNZD movement occurs during the Asian session because that’s when most of the economic data from New Zealand and Australia is released. The Asian session begins at 10 pm GMT when Sydney opens, but trading volumes increase at midnight GMT when Tokyo opens.
Most of the trading activity usually occurs when there is a trading session overlap. Tokyo and London overlap for an hour as the Asian session closes and the London session opens. During this time, the market usually has more active traders and it’s also generally more liquid. With more liquidity, slippage is less likely and spreads may even be reduced.
Popular Trading Strategies for AUDNZD
You can trade AUDNZD using various strategies. The top AUDNZD trading strategies include:
Trend Trading
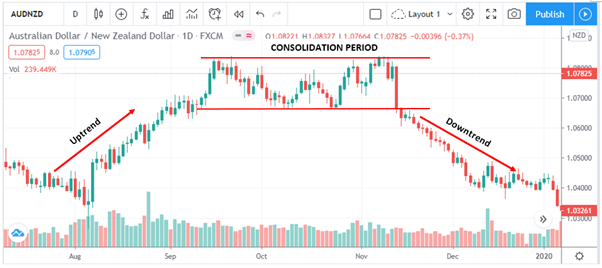
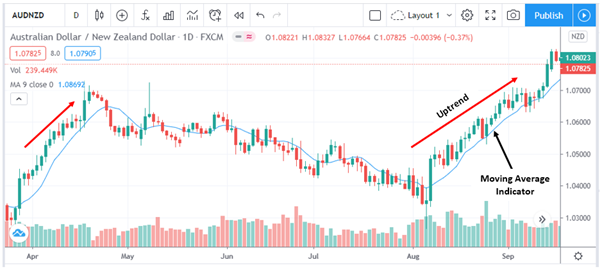
Trend trading is about using technical indicators to identify the direction of market momentum i.e. identifying a market’s uptrends and downtrends. AUDNZD makes a good candidate for trend trading because it tends to trend strongly, with clear consolidation periods.
You can use moving averages to see the pair’s underlying trend. For example, you can buy when the current price goes below the moving average and sell when the price peaks above the average.
Swing trading
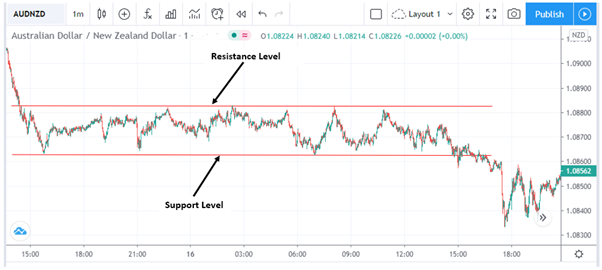
Trend trading is typically a longer-term strategy (typically months). If you want a shorter-term strategy that usually runs for a couple of days to weeks, swing trading may work better for you.
With swing trading, you identify ranges then you buy at support levels and sell at resistance levels.
Position Trading
Position trading involves holding on to a trade for an extended period, usually over several weeks to years, with the expectation that the investment’s value will increase. This strategy ignores short-term price movements in favor of longer-term trends and greater profit potential.
Since AUDNZD tends to trend a lot strongly for relatively long periods, you can try to capture more profits from longer-term trending moves.
However, you have to remember by encompassing a long time frame, position trading increases the trade’s inherent risk.
Note: It’s easy to confuse trend trading with position trading, but they are different. The former is strongly hinged on technical analysis while the latter mainly focuses on fundamental analysis.
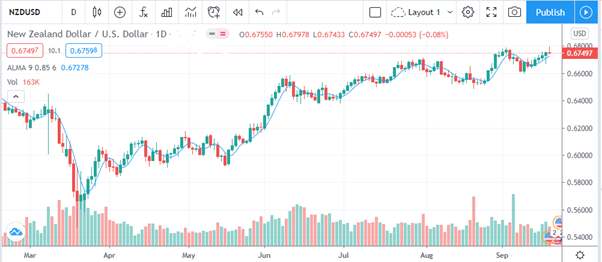
AUDNZD tends to rise and fall similar to AUD/USD and NZD/USD. This is likely because of the many similarities between the factors that influence the movement of both the Australian dollar and New Zealand dollar.
Here’s a quick look at how similar the movements of these three currency pairs are.
AUDNZD Chart
NZDUSD Chart
AUDUSD Chart
Note: Currency pair correlations are dynamic and will always be changing due to various political and economic factors. It’s important to keep up with shifting currency relationships.
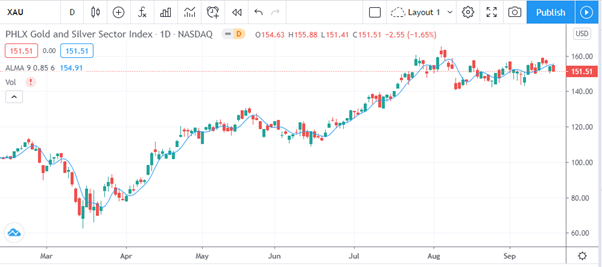
Correlation of AUDNZD with other commodities, instruments, or indices
The reliance of New Zealand’s and Australia’s economies on commodity exports means that price movements of the commodities produced in each country will likely impact the price of AUDNZD.
AUDNZD Chart
XAU (Gold) Chart
Also, since Australia is among the world’s biggest gold producers and exporters, gold prices normally affect AUDNZD. This means that when gold prices increase, the price of AUDNZD will probably increase, and vice versa.
Related Questions
The following are some questions related to AUDNZD.
What is the highest AUD has ever been?
AUD hit a record high on 27 July 2011 when it traded at 1.1080 versus the U.S. dollar.
What is the best time to trade AUD/USD?
The prime trading hours for the AUD/USD currency pair are generally between 7 pm and 4.30 am GMT. During these times, you’re able to take advantage of movements in both the American and Asian sessions.