EURNZD is often underestimated and associated with high risk. But with the right knowledge and trading strategy, this pair is a noteworthy trade vehicle with high-profit potential.
To trade EURNZD:
- Learn how the EURNZD pair works
- Choose a broker and open an account
- Analyze EURNZD
- Build your trading plan and select a trading platform
- Open and monitor your EURNZD position
- Close the trade
The EURNZD pair can make wide swings each day. What’s more, the pair’s volatility can exceed that of the more popular currency pairs, providing more opportunities to potentially make more significant profits. So how exactly does this pair work?
Table of Contents
Currency Pair Chart and Profile
EURNZD shows the value of the euro against that of the New Zealand dollar. The euro is among the world’s strongest currencies and the official currency of 19 European Union (EU) countries that constitute the Eurozone. On the other side is the New Zealand dollar, one of the world’s high-yielding commodity currencies. The EURNZD pair is also known as the Euro Kiwi.
The economies behind EURNZD
New Zealand has a GDP ranking of 52. Australia and the EU are among New Zealand’s top trade partners. The country also shares major ties with Asian countries, especially China, such that it’s often considered a proxy for Chinese growth.
The country’s economy and the value of the New Zealand dollar are both centered on tourism and exporting commodities. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ), which is the central bank of New Zealand, is in charge of the country’s monetary and fiscal policy.
The EU economy is the joint economy of the member states of the EU. It’s the second-largest economy in the world, rivaled only by the U.S economy. The European Central Bank (ECB) is the Eurozone’s central bank. In addition to making EU monetary policy decisions, the ECB is also in charge of keeping the euro stable.
What influences the movement of EURNZD?
The EURNZD pair is influenced by events that affect Eurozone countries. This can include things such as major crises in the European countries or political factors such as elections in one of the Eurozone countries. Additionally, the euro is affected by commercial releases of the ECB, and so you should be on the lookout for these when trading EURNZD.
The movement of the New Zealand dollar also plays a significant part in influencing the movement of EURNZD. For example, since Australia and China are New Zealand’s key trade partners, the economic performance of both countries has a substantial impact on New Zealand’s. Additionally, changes in other elements that influence New Zealand’s economic performance also affect EURNZD.
The commodity market
Because New Zealand relies heavily on commodity exports, the NZD is a commodity currency. Increasing commodity prices will cause the value of NZD to rise and this will impact the movement of the EURNZD pair. It’s important to monitor changes in the commodity market when trading EURNZD.
Surge in exports
Increasing demand for New Zealand’s products usually boosts New Zealand’s GDP and the value of the NZD. This, in turn, influences the value of EURNZD.
Weather conditions
Wool, meat, and milk are New Zealand’s major exports. As such, the agricultural industry is a big driver of New Zealand’s economy. Severe weather conditions such as drought or floods will have a significant negative impact on the economy and this will affect the performance of EURNZD.
Is EURNZD an exotic pair?
Currency pairs that contain all the other major currencies except the U.S. dollar are called minors, cross-currency-pairs, or crosses. Since this is the case with EURNZD, the pair is a minor currency pair and one of the Euro crosses.
Pros of trading EURNZD
Perhaps the biggest advantage of trading EURNZD is the fact you can capitalize on the pair’s volatility. Nonetheless, the pair also has several other merits.
- The EURNZD cross can provide more trading opportunities compared to the major forex pairs bound to the U.S. dollar. While the majority of the forex market trades on pro- and anti-U.S. sentiment, you can insulate your trades against U.S dollar price movements and U.S. news releases by trading EURNZD.
- Cross pairs like the EURNZD pair tend to develop stronger trends compared to the major pairs. The strong trends are usually created by diverging interest rate expectations between the two non-U.S. currencies.
- EURNZD allows traders to carry trade short positions. This is due to the significant difference in refinancing rates of the euro and New Zealand dollar.
Cons of trading EURNZD
- EURNZD isn’t one of the commonly traded pairs, therefore, it has relatively lower liquidity. Nearly all the major forex pairs provide ample liquidity and minor transaction costs, but the less common pairs such as EURNZD can be costlier to trade.
- Trading EURNZD can attract wider spreads due to the pair’s high volatility.
- EURNZD has an added layer of risk because it doesn’t include the U.S. dollar. Because the U.S. dollar is a major currency, it’s usually easier to evaluate the financial and political stability of one country against the U.S. Since EURNZD is a minor pair, its evaluation is relatively harder. Having little knowledge of the Eurozone and New Zealand socio-economic and political conditions can wreak havoc on your trading strategy.
The Best Time to Trade EURNZD
The New Zealand dollar normally sees the most movement when the Asian session is open while Eurozone economic data is generally released at 6 am GMT. The euro is most actively traded up to three hours after this data release. As a result, the best time to trade EURNZD is most likely during the European session and when the Asian and European sessions overlap between 8 am and 9 am GMT.
Best Trading Strategies for EURNZD
In general, the EURNZD cross is a reasonably predictable and stable pair. The top trading strategies for the pair include:
Trend Trading
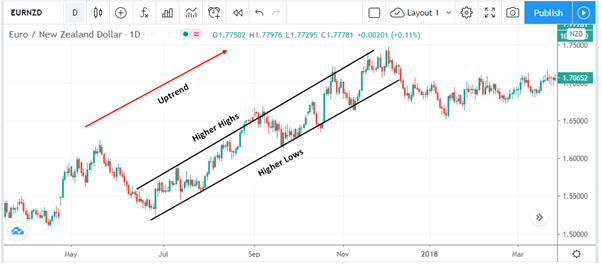
A trend occurs when the price of a currency pair moves in a particular direction over a period of time. Since EURNZD tends to form medium-term trends, you can identify these and position yourself for potentially profitable entry and exit points.
For instance, you can identify an uptrend with a series of higher highs and higher lows. Conversely, a downtrend is a series of lower highs and lower lows.
Pullback trading
A pullback is a short-term move against the longer-term trend. This move can offer an opportunity to join the trend at a relatively favorable price.
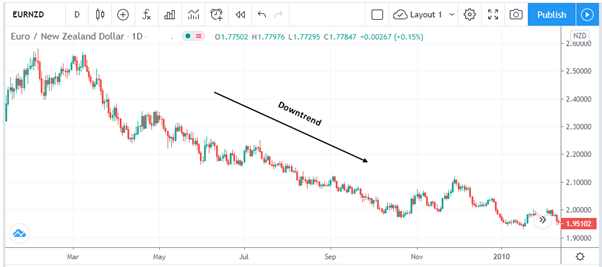
When trading a pullback, you can look for a break in the trend line before entering a trade. For instance, in the following example, EURNZD is in a downtrend, so you can short when the price breaks the trend line.
Pullback trading is essentially based on the idea of selling high and buying low. When trading pullbacks in a downtrend, you’re basically selling high and in an uptrend, you’re buying low. The biggest downside of pullback trading is that you may miss the move.
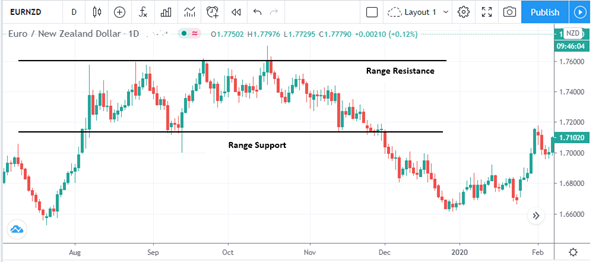
Range trading
Range trading is about identifying levels that act as the support and resistance for a range on a chart. You will then need to stay alert for when the price nears either of these levels.
For instance, when the price nears the resistance level and you think the resistance will hold, you can sell (go short). Conversely, if the price is nearing the support level which you think will hold, you can buy (go long). If the price continues to fall below support, you can go short since the support level will have failed to hold.
In addition to Australia and New Zealand’s proximity, the interconnection and similarity of the two countries’ economies mean that EURNZD strongly correlated with EURAUD.
EURNZD also has a strong inverse correlation with NZDUSD.
Correlation of EURNZD with other instruments or commodities
Australia is New Zealand’s biggest trading partner and so New Zealand is highly susceptible to movements in Australia’s economy. For instance, since Australia is one of the top gold producers in the world, and gold price movements affect its economy, the EURNZD pair tends to be affected by gold prices. EURNZD is also affected by the value of other commodities such as silver since NZD is a commodity currency.
Related Questions
Some of the questions linked to the EURNZD pair include:
What time does the euro start trading?
The euro starts trading during the European forex session which typically runs from 7 am to 4 pm GMT. You can check or Forex Market Hours guide for more information.
How do you trade a highly volatile forex pair?
Trading a volatile pair like EURNZD can be challenging. However, you can improve the trading by remembering the following:
- Big news events can influence a currency pair’s volatility. The same is also true for data releases. You can improve your chances of succeeding when trading a volatile forex pair by keeping up with big news updates and using an economic calendar to stay ahead of data releases. This will help you better forecast possible changes in volatility.
- Volatile currency pairs still obey several technical aspects of trading such as trend lines and support and resistance levels. You can leverage technical analysis and robust risk management rules to trade the pair’s volatility.